Veronika Vitazkova
Flutist and recording artist

I offer recordings of the following instruments

Concert Flutes
The Western concert flute is a family of transverse side-blown woodwind instruments made... of metal or wood. It is the most common variant of the flute. The concert flute in C, the piccolo (plays an octave higher than the regular treble flute.) And the lower member of the flute family is the alto flute in G.

Duduk
The duduk which means “apricot-made wind instrument”, is an ancient ... Armenian double reed woodwind instrument made of apricot wood. It is indigenous to Armenia.

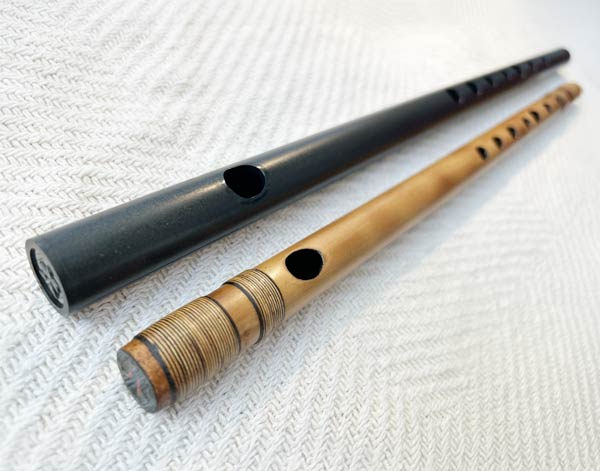
Tin Whistle
The tin whistle, also called the penny whistle, is a simple, six-holed woodwind instrument.... It is a type of fipple flute, putting it in the same class as the recorder, native american flute, and other woodwind instruments that meet such criteria.

Low Whistle
The irish low whistle, or concert whistle, is a variation of the traditional tin ... whistle/pennywhistle, distinguished by its lower pitch and larger size. The expression "Irish low whistle" is not denoting an Irish origin, but just an intensive use of this instrument in Ireland and, because of cultural similarity, in the whole British isles.

Fujara
The fujara, also known as the ''queen'' of Slovak folk instruments, is an overtone ... flute from central Slovakia played originally by shepherds.

Koncovka
The koncovka is a slovak overtone fipple flute traditionally played by... shepherds throughout the Carpathian Mountain region of Slovakia.

Dvojačka
The dvojačka, also dvojačky, dvojanka is a double shepherd flute from Slovakia, it is a... combination of a 6-hole shepherd’s flute with an overtone flute. A player blows simultaneously to both pipes, one of them having a function of a melodic pipe, the other playing a constant drone.

Slovak Folk Flutes
Slovak shepherd 6-hole traverse flutes (priečne píšťaly), traditionally played... by shepherds throughout the Carpathian Mountain region of Slovakia.

Gajdica
Gajdica is an archaic instrument, which was preserved in Lipany, a village ... in rural countryside of Saris region (Slovakia). It consists of a wooden pipe with a cowhorn bell at the lower end.
Ney
Is an end-blown flute that figures prominently in Middle Eastern music. In some of ... these musical traditions, it is the only wind instrument used. The ney has been played continually for 4,500–5,000 years making it one of the oldest musical instruments still in use.

Dizi
The dizi (笛子) a chinese bamboo flute is one of the most popular instruments in ... traditional chinese music.

Shakuhachi
The shakuhachi (Japanese: 尺八) is a Japanese and ancient Chinese longitudinal, ... end-blown flute that is made of bamboo. It is derived from the Chinese bamboo-flute. The bamboo-flute first came to Japan from China during the 7th century.

Bansuri
A bansuri is a side blown bamboo flute originating from the Indian subcontinent. ... The word bansuri originates in the bans (स) [bamboo] + sur (सुर) [melody].

Schwegel
Schwegel, from Old High German suegala, “shin bone ” (also called fife) has been a ... simple form of a longitudinal flute or transverse flute since the Middle Ages. It was used in some folk music traditions to accompany dancing by all social classes.
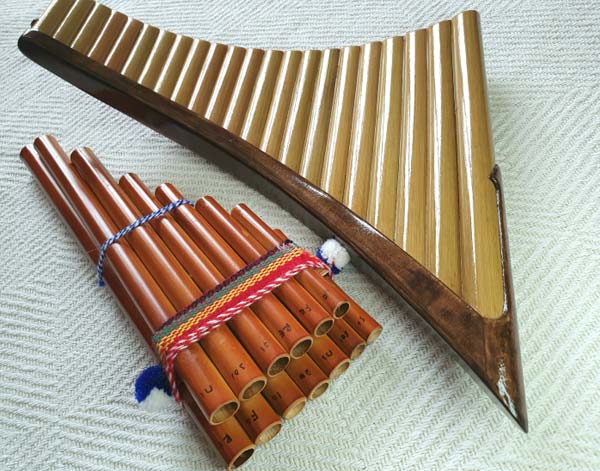

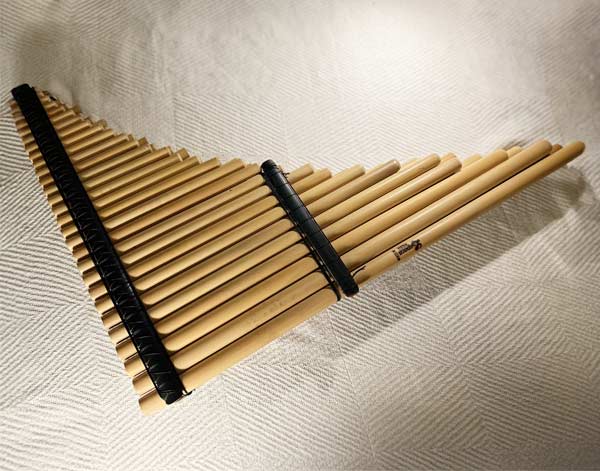
Pan Flute
A pan flute (also known as panpipes or syrinx) is a musical instrument based on the... principle of the closed tube, consisting of multiple pipes of gradually increasing length (and occasionally girth).
Moseño
Mohoceño, moceño, moxeño, moheño, is found in the region of Canton Mohosa in Bolivia.... principle of the closed tube, consisting of multiple pipes of gradually increasing length (and occasionally girth).

Native American Flute
The Native American flute (also called a love flute) is a flute that is haeld in front... of the player, has open finger holes, and has two chambers: one for collecting the breath of the player and a second chamber which creates sound. The player breathes into one end of the flute without the need for an embouchure. From the earliest days until the present time, the indigenous people of North America have incorporated music into their spirituality, celebrations, and everyday lives.

Zurna
Zurna is a widely used instrument in Turkey as well as in West and Central Asia, ... South-Eastern Europe and North Africa under very similar names like sorna, surnay, zurla etc. It is a double-reed woodwind instrument which has a very bright, high frequency sound.

Kaval
The Kaval is an end-blown flute and it’s one of the oldest folk instruments in Europe, ... that’s why its exact origins are not known. It is known, though, that its predecessors are the Egyptian, Syrian and later Greek wind instruments. The word ‘kaval’ itself comes from Turkish and it means “pipe”. Different variations of the instrument exist in the Balkans, Armenia, Turkey and the Middle East. The kaval is primarily associated with mountain shepherds.Unlike the transverse flute, the kaval is fully open at both ends, and is played by blowing on the sharpened edge of one end.
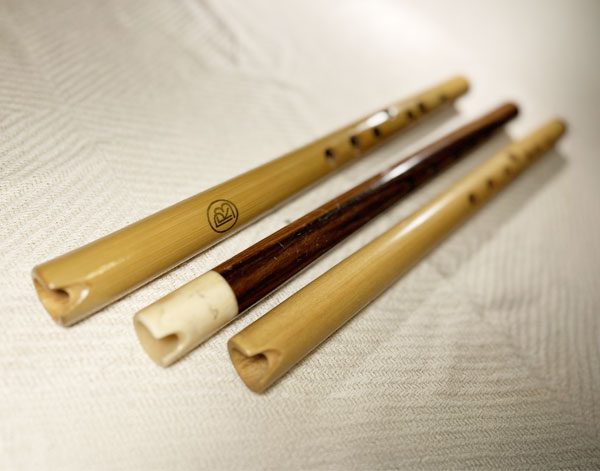

Quena
The quena is a traditional Andean flute made from wood or bamboo. It is an ... end-blown flute with six front finger holes and one thumb hole on the back. The quena produces a soft, breathy sound and is commonly used in the folk music of countries like Peru, Bolivia, and Ecuador. Its distinct, melancholic tone is well-suited for both solo performances and ensemble music, often accompanying traditional Andean instruments like the charango or panpipes.
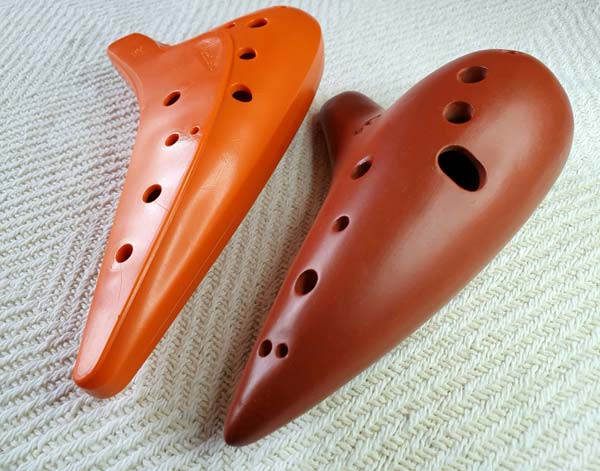

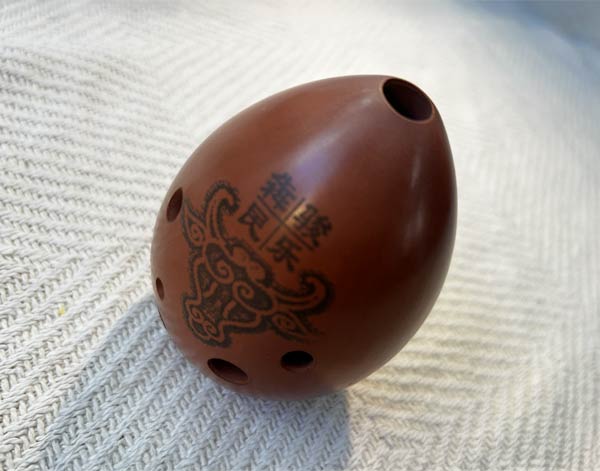
Ocarina
The ocarina belongs to a very old family of instruments, believed to date back over ... 12,000 years. Ocarina-type instruments have been of particular importance in Chinese and Mesoamerican cultures. Different expeditions to Mesoamerica resulted in the introduction of the ocarina to the courts of Europe. The modern European ocarina dates back to the 19th century.

Didgeridoo
The didgeridoo is a wind instrument, developed by Aboriginal peoples of ... northern Australia at least 1,500 years ago, played with continuously vibrating lips to produce a continuous drone while using a special breathing technique called circular breathing.
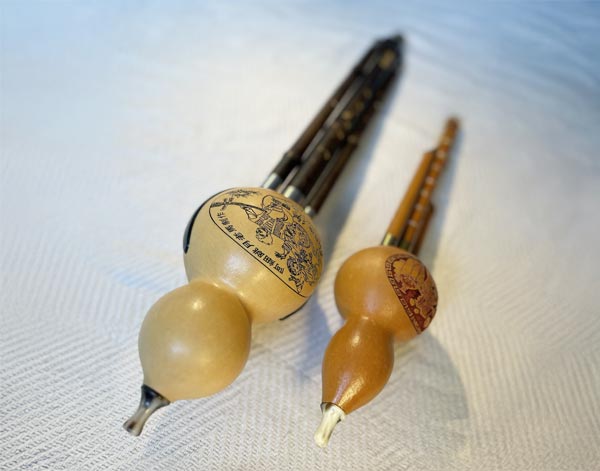
Hulusi
The hulusi (traditional: 葫蘆絲; simplified: 葫芦丝; pinyin: húlúsī), also known ... as the cucurbit flute and the gourd flute is a free reed wind instrument from China, Vietnam and the Shan State and by the indigenous people of Assam. It is held vertically and has three bamboo pipes that pass through a Calabash gourd wind chest; the center pipe has finger holes and the outer two are typically drone pipes. It is not uncommon for a hulusi to have only one drone pipe while the second outer pipe is merely ornamental. The drone pipe has a finger hole which allows it to be stopped.
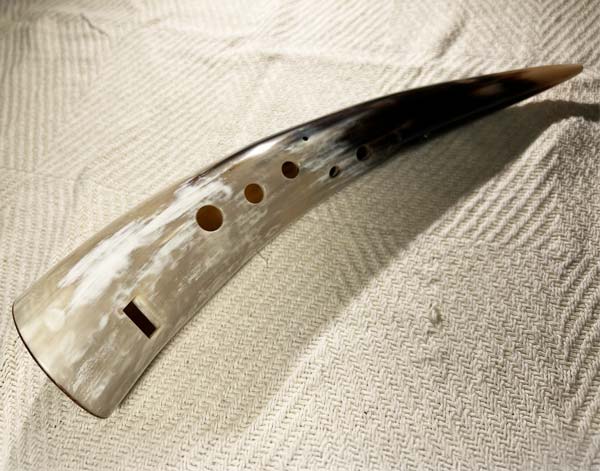

Gemshorn
The gemshorn is a medieval wind instrument traditionally made from the horn of ... a chamois or other animals like cows. It is an end-blown flute-like instrument with finger holes along its length, similar to a recorder. The gemshorn produces a soft, mellow tone and was popular in Europe during the Middle Ages and Renaissance. Though it fell out of use for a time, it has been revived for historical music performances today.
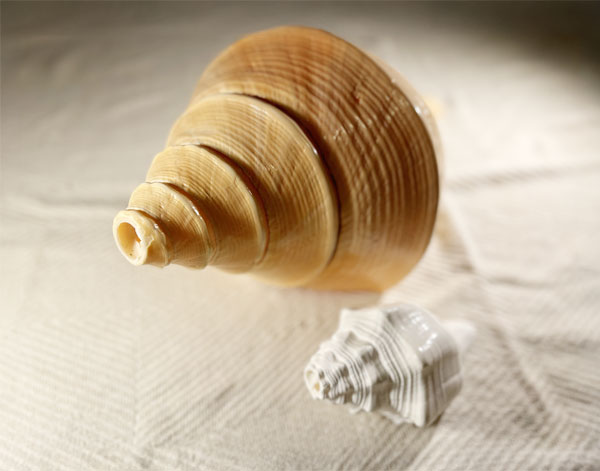

Conch Shell
The conch shell (also known as a conch horn) is a natural wind instrument made from ... a large sea snail shell. It has been used in various cultures around the world, particularly in coastal regions, for thousands of years. By cutting off the tip of the shell and blowing into it, similar to a brass instrument, the conch produces a powerful, resonant sound. It is used in ceremonial, signaling, and musical contexts, notably in regions like the Pacific Islands, South Asia, and the Caribbean. The pitch and tone can vary depending on the size and shape of the shell.
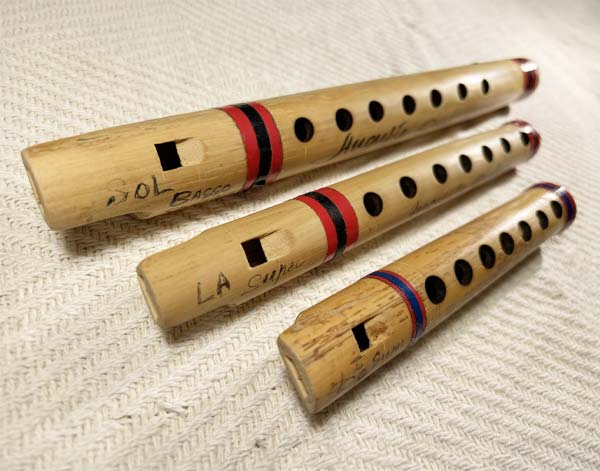

Friscalettu
The friscalettu is a traditional Sicilian wooden flute, often made from cane or reed. ... It is a small, end-blown flute with six or seven finger holes, producing a bright, clear tone. The friscalettu is commonly used in Sicilian folk music, accompanying dances and songs, and is often played in festive or rural settings. Its sound and technique are similar to other folk flutes, and it can be used for both melodic and rhythmic playing, making it a versatile instrument in traditional Sicilian ensembles.
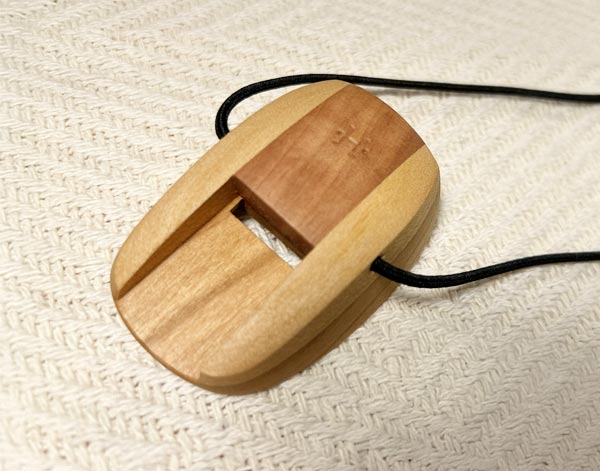

Nose Flute
The nose flute is a simple wind instrument played by blowing air through the nose ...into a small mouthpiece. The player covers finger holes to change the pitch, similar to other flutes. Found in various cultures, particularly in Polynesia and Southeast Asia, the nose flute is often used in traditional ceremonies and storytelling. Its sound is soft and melodic, and it has cultural significance, symbolizing purity or emotions in some traditions.

The Xun (壎 / 埙)
Origin of this unique wind instrument dates back to the Stone Age and has much
... to do with early Chinese hunting practices. During ancient times, people often tied a stone or mud ball to the rope that was used for hunting wild animals. Some of the balls were hollow, which allowed it to make many sounds when thrown. Most people found it enjoyable and learned how to blow air into it. Gradually, the "stone meteor" became the musical instrument we know as "xun".
The use of xun in Chinese history was found mainly in the performance of palace music. However, the sound of xun is also associated as the symbol of respectable hermits, lady in sorrow, or heroes at the end of their strength, and is considered the best instrument to perform a heartbreaking tone, or to make solemn music within the royal court. The sound of xun represents a particular beauty, which combines with loneliness, desolate and elegance.

Zampoña / Siku
The zampoña, also known as the siku, is a traditional Andean panpipe made of a series ... of bamboo or reed tubes of varying lengths, bound together in two rows. Each tube produces a different pitch, and players alternate between the two rows to create melodies. The instrument is commonly used in the folk music of the Andes, especially in Bolivia, Peru, and northern Chile. Its airy, resonant sound is iconic in Andean ensembles, often played alongside drums and string instruments like the charango.

Diaulos
The launeddas and the diaulos are both ancient double-reed woodwind instruments,
... but they have distinct cultural and historical backgrounds.
The launeddas originated in Sardinia and are still played in traditional Sardinian music today. They consist of three pipes: two melody pipes and one drone pipe. The performer uses circular breathing to play all three pipes simultaneously, creating a unique and haunting sound. The launeddas have a long history in Sardinian culture, dating back to ancient times, and they were likely influenced by various Mediterranean cultures.
On the other hand, the diaulos originated in ancient Greece and consisted of two parallel pipes, each with its own mouthpiece. The diaulos was commonly used in religious ceremonies, festivals, and theatrical performances in ancient Greece. It had a significant cultural and musical role in Greek society but eventually fell out of use after the decline of ancient Greek civilization.
While both instruments are double-reed woodwinds and may share some similarities in sound and construction, they come from different regions and cultural contexts. However, they both represent the rich diversity of ancient musical traditions in the Mediterranean region.

Hichiriki
The hichiriki is a traditional Japanese double-reed wind instrument, made of ...bamboo. It has a short, cylindrical body and produces a strong, piercing sound. The hichiriki is a key instrument in gagaku, the classical court music of Japan, where it plays the main melody. Despite its small size, the hichiriki’s unique timbre is highly expressive and central to Japanese traditional music.

Bawu
The bawu is a traditional Chinese wind instrument, commonly found in the ...folk music of the Yunnan province and surrounding areas. Though it is played like a flute, it is actually a free-reed instrument, with a single metal reed inside its bamboo body. The bawu produces a soft, mellow sound, often described as haunting and soulful. It is typically used for expressive, melodic lines in Chinese folk music, and can be played solo or within an ensemble.

Xiao
The xiao is a traditional Chinese end-blown flute made from bamboo. It has a long, ... slender body with five or six finger holes, producing a soft, mellow, and airy sound. The xiao is known for its serene, meditative tone and is often used in Chinese classical and folk music, as well as for solo performances. Its calming sound makes it a popular instrument for expressing emotions and peaceful landscapes in music.
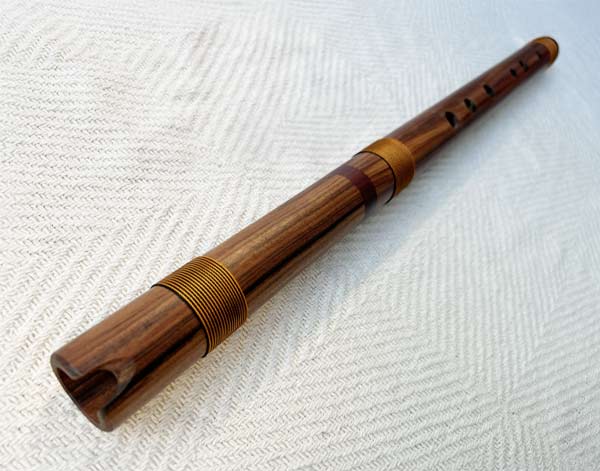
Gaita Hembra
The gaita hembra is a traditional Colombian wooden flute used in folk music, particularly ...in cumbia and gaita ensembles. It is typically made from cane and features a natural reed mouthpiece. The gaita hembra plays the melody and has a rich, warm tone, contributing to the lively sound of Colombian music. Its design allows for expressive playing, making it an essential instrument in festive celebrations and cultural performances.

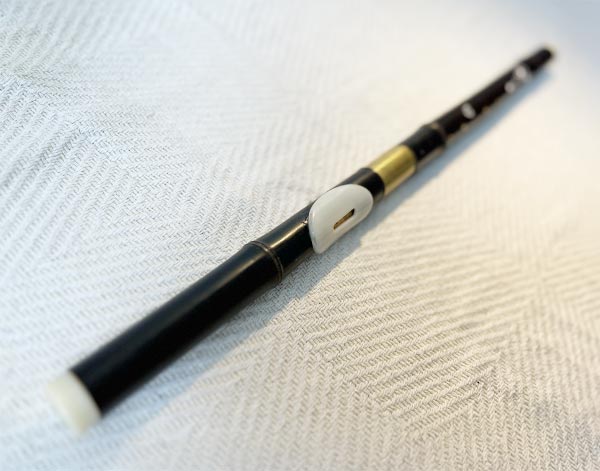
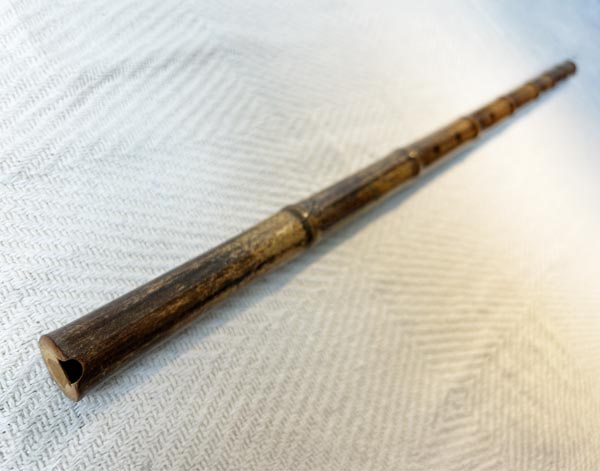
Quenacho
The quenacho, also known as kenacho, is a traditional Andean wind instrument, a type of
...flute used in South American music. It is larger than the quena, another popular Andean flute, and is characterized by its deep, resonant sound.
The quenacho is an important instrument in Andean folk music, particularly in the regions of Bolivia, Peru, and northern Argentina. It is commonly used in both solo performances and ensembles, often accompanying other traditional instruments like the charango (a small stringed instrument) and panpipes. Its sound is emblematic of the Andean highlands and is often used in music that evokes the natural landscapes and cultural heritage of the region.
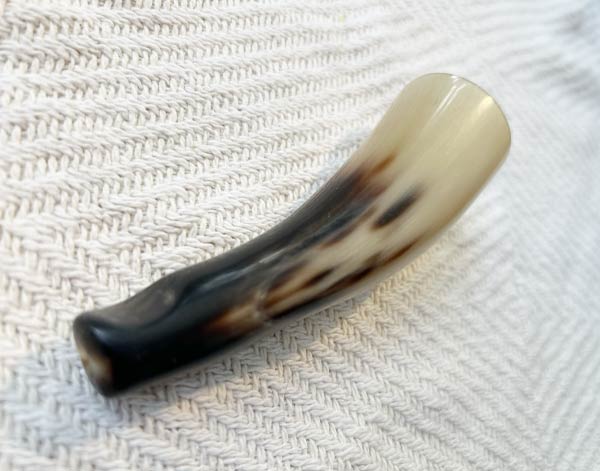

Troete
A tröte made from a horn is a simple, handmade wind instrument crafted from ...an animal horn, similar to a natural horn. By blowing into a small hole in the horn, it produces a loud, resonant sound used for signaling or ceremonial purposes. Traditionally, such horns have been used in rural areas for communication, herding, or as musical instruments in folk traditions. The sound is deep and raw, reflecting its natural material and craftsmanship.

Shinobue
The Shinobue is a traditional Japanese side-blown bamboo flute, commonly used ... in Japanese folk music, festivals, and the classical Noh and Kabuki theaters. It has a bright, high-pitched sound, and its tuning varies between two types: Uta (song) and Hayashi (festival or ensemble) flutes. The Shinobue can produce both lively and soulful tones, contributing to its versatility in various cultural performances.

Nokhan
The nohkan is a traditional Japanese bamboo flute used in Noh and Kabuki theater ...performances. It is an end-blown flute with a distinctive high-pitched, piercing tone. Unlike most flutes, the nohkan has an internal tube that creates dissonant overtones, giving it a unique, expressive sound that enhances dramatic scenes in the theater. Its sharp, bright sound is essential to setting the mood in traditional Japanese performances.

Ryuteki
The ryuteki, also known as the “dragon flute,” is a traditional Japanese transverse ...bamboo flute used in gagaku, Japan’s classical court music. With seven finger holes, it produces a bright, high-pitched sound meant to evoke the image of a dragon soaring between heaven and earth. Its lively, clear tone plays a key role in gagaku ensembles, often carrying the melody in ceremonial and imperial music.
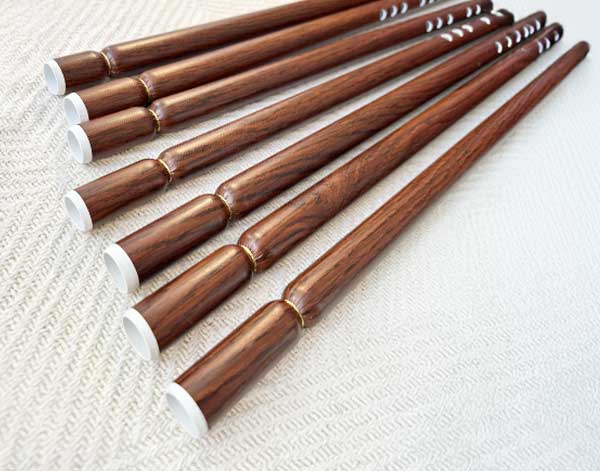

Arabic Ney
The Arabic Ney is an ancient, end-blown flute made from a hollow reed or cane. It is ...widely used in Arabic, Persian, Turkish, and other Middle Eastern music traditions. Known for its warm, breathy tone, the Ney has six finger holes on the front and one on the back, giving it a unique, soulful sound that can be both expressive and meditative. The Ney is a key instrument in classical Arabic music, especially in Sufi traditions, and requires skilled breath control to produce its distinct sound.
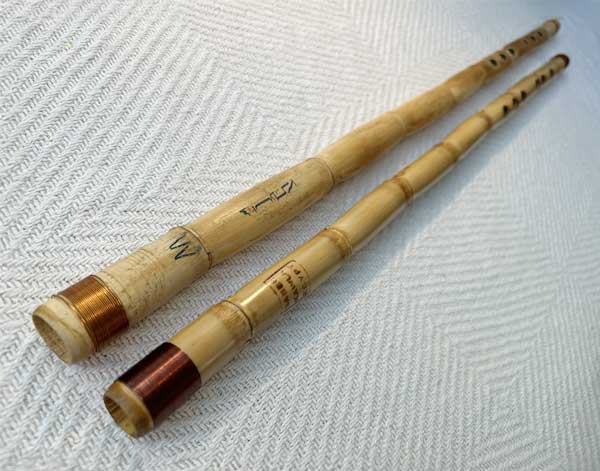

Persian Ney
The Persian Ney is a traditional end-blown flute widely used in Persian classical and ... folk music. Made from a hollow reed, it has six finger holes (five in the front and one in the back), producing a soft, airy, and deeply emotive sound. The Ney requires precise breath control, and it is capable of producing a wide range of pitches and subtle tonal variations. It plays a significant role in Persian spiritual and classical music, often accompanying Sufi poetry and meditative performances, symbolizing a connection to the divine.

Turkish Ney
The Turkish Ney is an ancient end-blown reed flute, central to classical Turkish music and ...Sufi spiritual practices. Made from a hollow cane, it typically has seven finger holes (six in the front and one in the back) and produces a warm, breathy sound that conveys deep emotion and spirituality. The Turkish Ney is known for its expressive tone and is played using a distinctive technique involving complex breath control. It has a rich cultural significance, often used in Mevlevi Sufi ceremonies (Whirling Dervishes) and Turkish classical music.

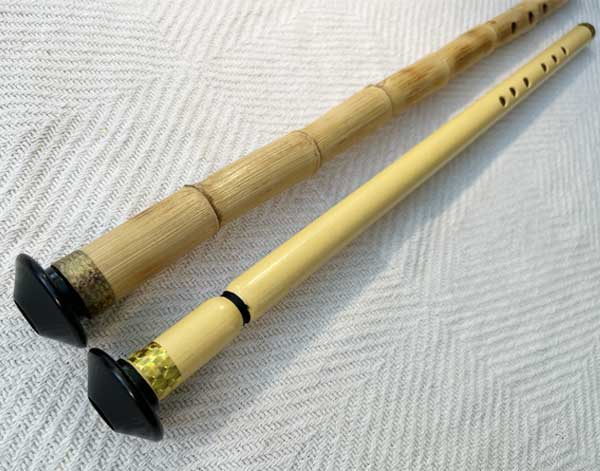
Moldovian Kaval
The Moldovian kaval has five and sometimes six holes and it is frequently used in ...traditional folk music both in Romania and Moldova.
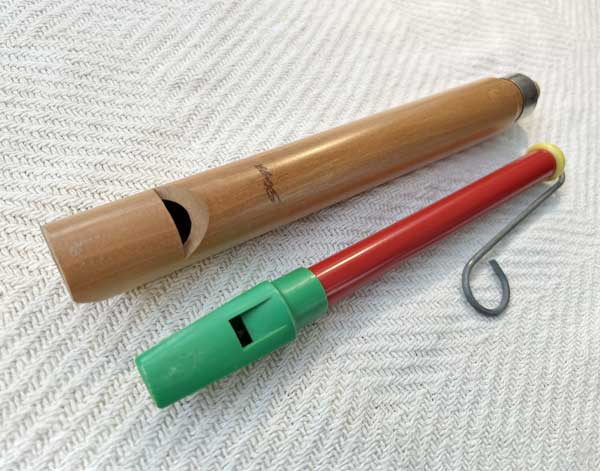

Lotus Flute
The Lotus Flute is a handcrafted bamboo flute designed by the Indian flutist ...Hariprasad Chaurasia, known for its mellow and soothing tones. It is crafted with precision to produce a pure, resonant sound, ideal for Indian classical music and meditative practices. The flute’s design is influenced by traditional bansuri flutes but with modifications that allow for greater tonal range and ease of play. Its warm and soft sound makes it popular for meditative and spiritual performances.

Coiok Amazonas
The Coiok Amazonas flute is a unique wind instrument, often crafted from bamboo cane, ... known for its ability to produce bird-like and nature-inspired sounds. Connected to the Amazon region, it holds a mystical quality, with roots in indigenous musical traditions. The flute is valued for its organic, enchanting tone, often used to mimic the sounds of nature, making it a distinctive instrument in traditional and spiritual performances.
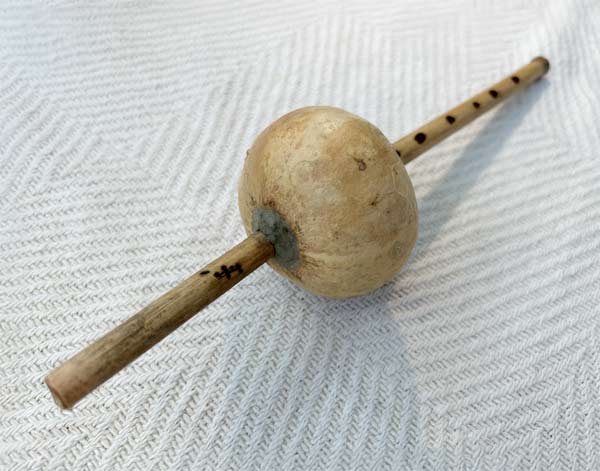

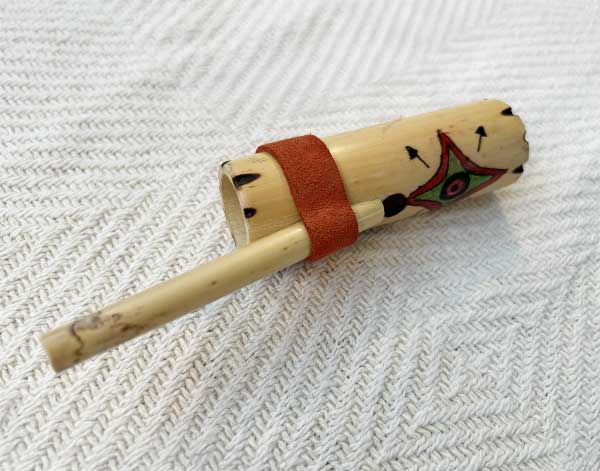
Pungi
The Pungi is a traditional Indian wind instrument, commonly associated with snake ...charming. Made from a gourd and two bamboo pipes, the Pungi produces a continuous, droning sound. It is played using circular breathing, allowing the performer to maintain an uninterrupted melody. The Pungi has a distinctive, reedy tone and holds cultural significance in folk music and religious rituals in India.
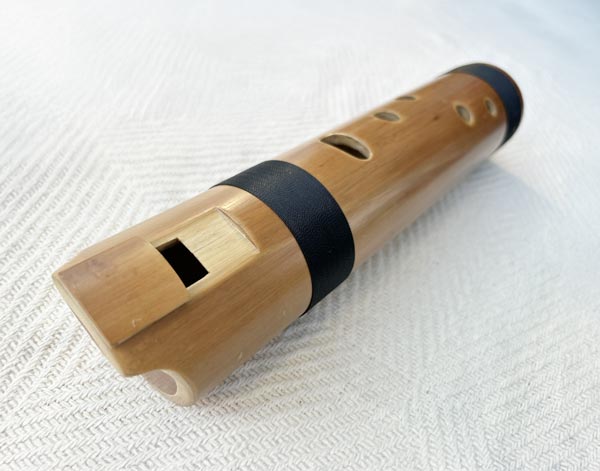

Wooden Ocarina
The wooden ocarina is a small, handheld wind instrument with an enclosed, hollow body ...and several finger holes. Crafted from wood, it produces a soft, mellow tone and is known for its simple yet expressive sound. The ocarina has been used in various cultures for folk music and can be played in different scales, making it versatile for a range of melodies. Its compact size and distinctive sound have made it popular in both traditional music and modern performances.
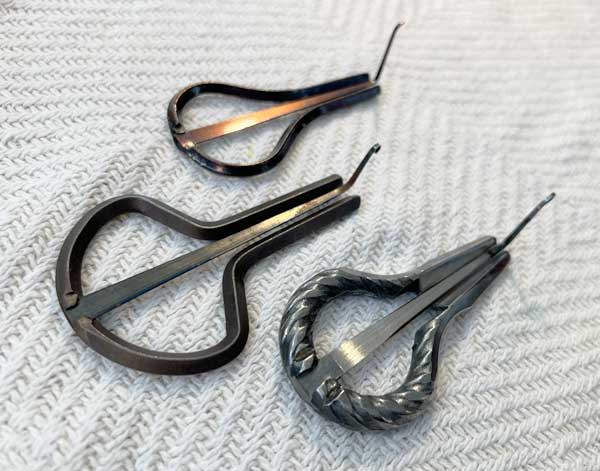

Mouth Harp
The mouth harp, also known as a Jew’s harp or jaw harp, is a small, plucked idiophone ...held between the teeth or lips. It produces sound by plucking a flexible metal or bamboo reed, with the pitch modulated by altering the shape of the mouth and breathing. Known for its distinctive twangy sound, the mouth harp is used in traditional music across various cultures and is often associated with folk, meditative, and shamanic performances due to its rhythmic, hypnotic tones.

Suona
The suona has a bright tone, a loud volume, and a wooden tube in a round and ... cone-shaped shape. The upper end is equipped with a copper tube with a whistle, and the lower end is covered with a copper bell mouth. The term suona derives from zurna, the Arabic name for the instrument. The penetrating sound of the suona, ideal for processions and military functions, was easily appropriated for popular music.. The player, whose mouth completely covers the small reeds, uses circular breathing (inhaling through the nose) to maintain a constant tone.
Bulgarian Kaval
The Bulgarian kaval is an end-blown wooden flute widely used in Bulgarian folk music. ...Made from wood, bone, or horn, it has eight finger holes (seven in the front and one in the back), and its open design gives it a rich, breathy sound. The kaval is known for its expressive range, capable of producing both soft, mellow tones and vibrant, lively melodies. It is traditionally used in pastoral music and folk dances, symbolizing the connection to nature and rural life in Bulgaria.
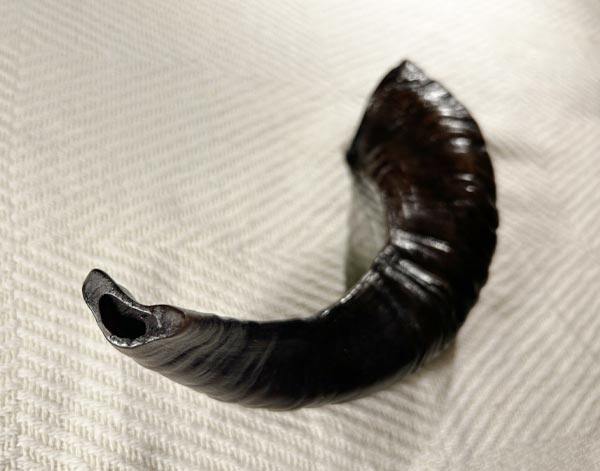

Shofar - Jewish Horn
The Shofar is an ancient Jewish horn made from a ram’s horn, traditionally used ...in religious ceremonies and rituals. Its sound is raw and powerful, often used to mark significant events such as the Jewish New Year (Rosh Hashanah) and the Day of Atonement (Yom Kippur). The Shofar is blown to inspire reflection, repentance, and spiritual awakening, and it holds deep symbolic meaning in Jewish culture, representing a call to action and connection with the divine.
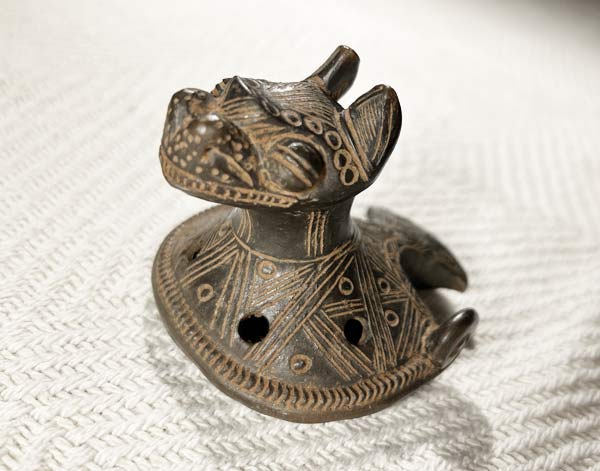

Aztec Ocarina
The Aztec ocarina is a small, ancient wind instrument made from clay, used by the ...Aztecs in ceremonial and ritual contexts. Shaped in various animal or human forms, it has multiple finger holes and produces a haunting, melodic sound. The Aztec ocarina’s tones are rich and expressive, often mimicking natural sounds like birds or wind. This instrument was an integral part of Aztec culture, used in music, storytelling, and spiritual practices.
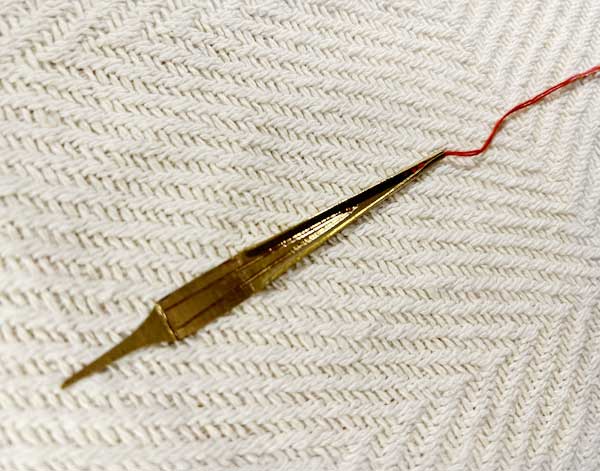
Vietnamese mouth harp / Đàn môi
The suona has a bright tone, a loud volume, and a wooden tube in a round and ... cone-shaped shape. The upper end is equipped with a copper tube with a whistle, and the lower end is covered with a copper bell mouth. The term suona derives from zurna, the Arabic name for the instrument. The penetrating sound of the suona, ideal for processions and military functions, was easily appropriated for popular music.. The player, whose mouth completely covers the small reeds, uses circular breathing (inhaling through the nose) to maintain a constant tone.
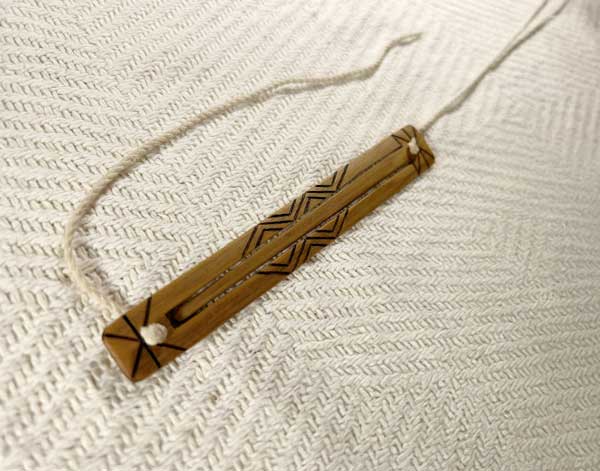

taiwanese mouth harp / Lubuw
The Taiwanese mouth harp, known as the Lubuw, is a traditional folk instrument ...made from metal or bamboo. Played by plucking a flexible tongue or reed while holding the instrument against the mouth, it produces a vibrant, resonant sound. The diyus are often used in Taiwanese indigenous music and are associated with cultural ceremonies, storytelling, and celebrations. Its distinct tones and rhythms reflect the rich musical heritage of Taiwan, making it a vital part of local musical traditions.
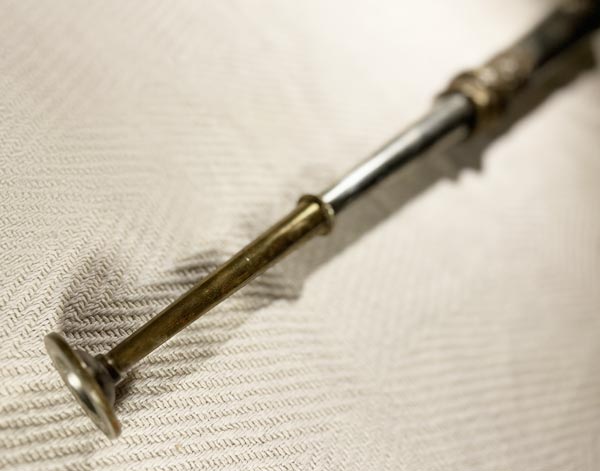

Tibetan horn / Dungchen
The Tibetan horn, commonly known as the dungchen, is a long, cylindrical brass ...or copper wind instrument traditionally used in Tibetan Buddhist ceremonies and rituals. Often measuring several feet in length, the dungchen produces deep, resonant tones that can be heard over long distances. Its sound is used to invoke a spiritual atmosphere, accompany chanting, and signal important moments during rituals. The dungchen is often ornately decorated, reflecting its cultural significance and connection to Tibetan spirituality and music.
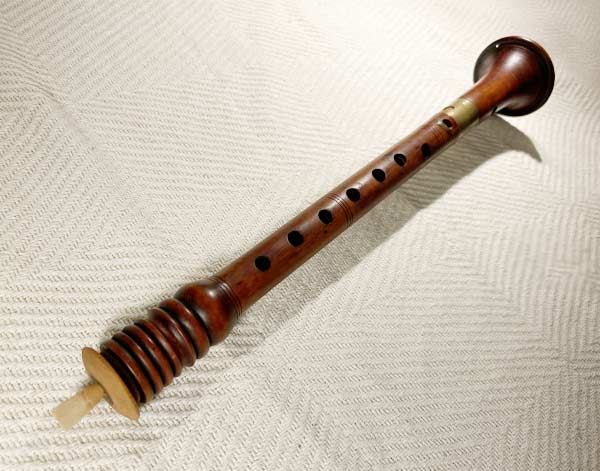

Shawm
The shawm is a double-reed woodwind instrument that originated in the Middle Ages ...and is considered a precursor to the modern oboe. It features a conical wooden body and a wide bell, producing a loud, piercing sound suitable for outdoor performances. The shawm was commonly used in European Renaissance and Baroque music, often in ensembles and dances. With its rich tonal qualities, the shawm evokes a sense of historical and ceremonial significance, frequently associated with festive occasions and military bands.
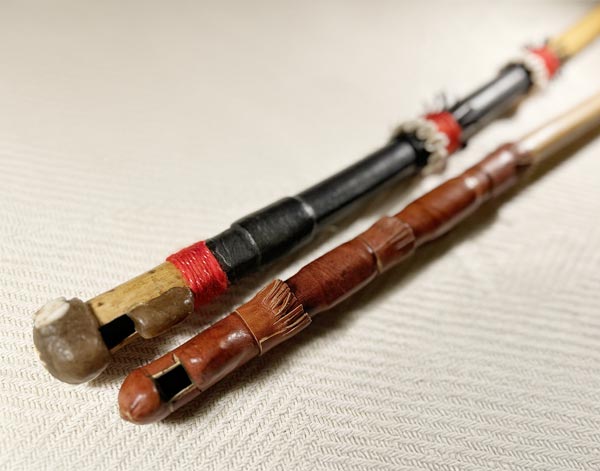

Tambin / Fula flute
The tambin, also known as the Fula flute, is a traditional flute of the Fula people from ... West Africa. Made from a hollowed piece of guinea corn or wood, it is an end-blown flute with three finger holes. Despite its simplicity, it produces a rich variety of melodic and rhythmic sounds. The tambin is used in traditional Fula music, often to accompany singing and dancing, and it holds a significant place in West African cultural expressions, particularly in Guinea, Senegal, and Mali.
The warbling bird whistle
The warbling bird whistle is a charming musical instrument crafted to replicate the
...melodious sounds of birds, typically made from ceramic. You need to put water into it so they create a trilling or warbling effect that closely mimics the birds.
They are often used in cultural ceremonies, for educational purposes, or simply as a delightful toy, the warbling bird whistle is both a functional and decorative piece.